The motherboard is the central part of the computer and is also known as a logic board or system board. It is the most significant component of the computer that controls all components of the computer system and establishes connections between them.
How to Build a Motherboard Step by Step?
IBM invented the first motherboard in 1981. It had some strange chips and in-house RAM with a processor. The company invented a baby AT motherboard in 1985. A motherboard is made of two materials.
- Fiberglass layer for insulation
- Copper forms lead pathways
The motherboards are made in layers to save space. It is composed of 4-8 layers of copper-embedded fiberglass that PCB makes motherboards significantly smaller to increase the speed of processing data.
Motherboard Manufacturing Process
The motherboard-making process is divided into five parts.

- Base Creation
- Surface Mount Technology (SMT)
- DIP (Dual Inline Package)
- Testing
- Packing
1) Base Creation
The layers of very complicated slices of fiberglass piled up together with a paste to form one solid layer. This layer of copper is coated on both the top and bottom sides. Then a light chemical photoresist is used to shape an etched copper trace on the PCB when exposed to light, and then it is coated on top of the copper layer.
After coating, a pattern covering specific components of the layer is placed on top before uncovering the entire slab to UV light. The uncovered parts of the copper layer are removed from the board by wash, exposing the almost-complete motherboard.
2) Surface Mount Technology
The motherboard uses a lot of components to make it. First, solder all SMDs (parts that do not have pins) on the board because they have electrical connections on the edges. Such as bios, resistors, audio, data chip, etc.
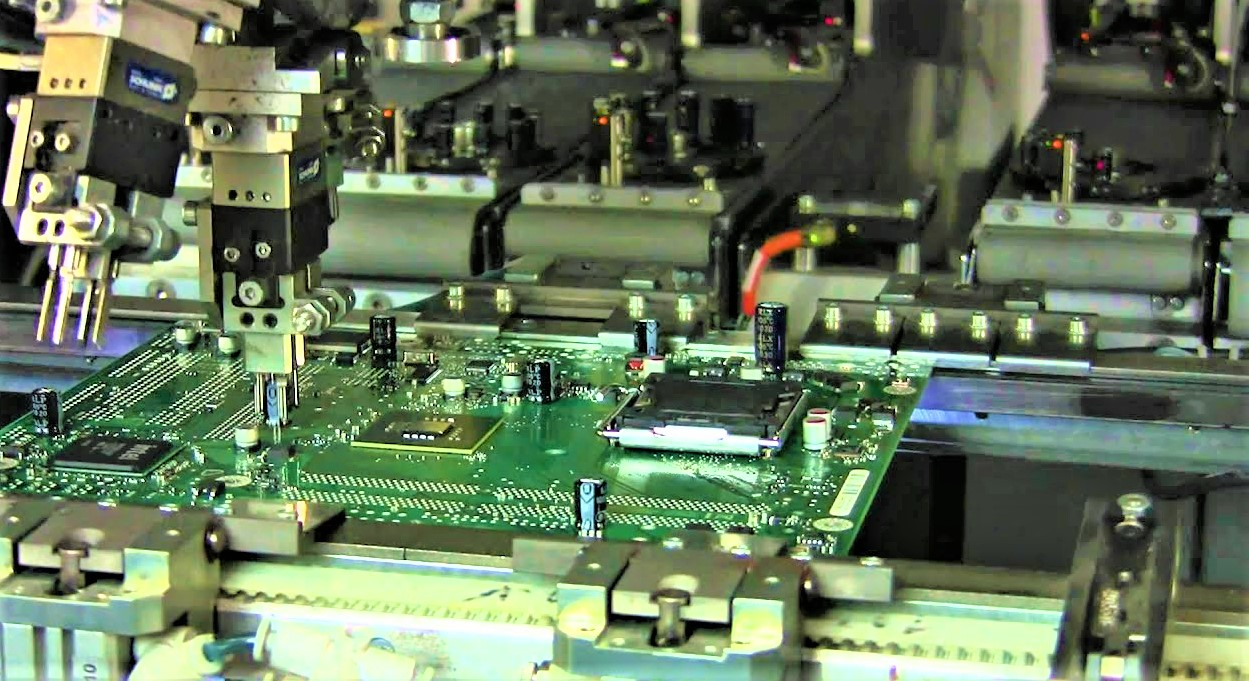
All parts of a motherboard have been coated with soldering paste to connect. This soldering paste acts like glue before going into the reflow oven for final soldering so that all components are in the accurate position before soldering. The high-speed chip placer is very fast and can place 5 to 10 components per second. Most components mounted by the motherboard making machine around a millimeter wide must be precisely placed on the PCB.
Nowadays, motherboards have components on both sides. The first side goes into the factory process as a reverse side. When the reverse side is done, a motherboard making machine switches the motherboard to the front side, and the process starts again on the SMT light. Before setting the Chip, it is verified to check if there is any problem. A machine places the chipset like audio, SATA, and USB ICs on the board. The same goes for the CPU socket.
3) Dual Line Package (DIP)
This stage is the second central process on a motherboard. All trim components and ICS has already been added. Now place all the other components that have pins going through the PCB. All parts of a motherboard are manually inserted during this state, such as connectors, power sockets, PCI Express, ram slots, solid capacitors, and CPU sockets, and then soldering correctly.
4) Testing Stage
Now the most extensive quality still needs to be checked. Again has been checked. The junction box allows easy switch on /switch off of the components. Once the UP board has passed all the testing and quality analysis, the boards are sent to the packing process.
5) Packaging
This is the final stage where it makes its way into the box you will see in the shop. Some packages are sold online on different purchasing platforms.
Major Motherboard Components
The significant parts of a motherboard are listed below.
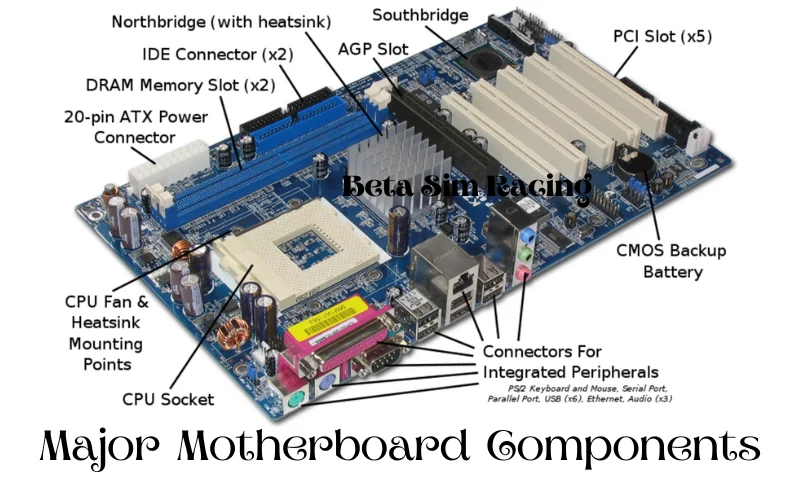
- CPU Chip: The central processing unit is the computer’s main processor that controls all functions and calculations.
- CPU Slot: A CPU slot or CPU socket is used to install the processor without soldering it. That provides mechanical and electrical connections between the PCB and microprocessor.
- DIMM RAM: RAM is a type of Computer memory. Ram keeps data easily manageable so that it can be retrieved quickly. DDR, DRM, SDRM, and SRM are types of RAM.
- BIOS: BIOS is a CMOS battery responsible for loading basic computer hardware and booting the Operating system & and provides runtime services for operating systems and programs. It also stores the time and data in it.
- USB Ports: The USB port (Universal Serial Bus) is easy to use and connects different computing devices such as Keyboard, Mouse, printers, speakers, etc. These ports are also available in Laptops.
- Parallel Port: In the past, the Old printers had a special connector called a Parallel port. It carries the data as opposed to the serial ports. The 25 pins female DB type connector is used in the parallel port to connect with the computer.
- I/O Port: These are two kinds of ports; Internal ports and External ports. The Internal ports connect the motherboard to internal devices, and the external ports connect the system’s motherboards to external devices.
- AGP Slots: The modern motherboards have ports that connect Graphic cards to a computer board. The AGP card used for 3D outputs.
- PCI Slots: The PCI slot is a built-in slot found on the motherboard that allows the addition of various hardware components such as modems, graphic cards, network cards, etc.
- Southbridge / Northbridge: These are core logic chips on the motherboard. Northbridge is connected to the CPU directly, and Southbridge is connected via Northbridge to the CPU. It manages the links between the cpu and other components of the motherboard.
- CMOS Battery: CMOS stands for Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor. It is found on laptops and desktops. It is also called the BIOS memory that stores the BIOS setting. The CMOS battery is responsible for storing the time, date, and data.
- Power Supply Connector: A power supply provides electric power to the computer. It converts the AC to DC power.
- Mouse and Keyboard Ports: All computers have keyboard and mouse ports connected directly to the motherboard. Previously PS/2 was using current USB connectors.
- ID Controller: The IDE is an interface standard used to connect hard drives, SSD drivers, CD/DVD, etc.
- ISA Slot: The ISA slot is issued to connect input devices and modems. It was an 8-bit and 16-bit bus, then extended to the EISA 32-bit bus and replaced by Vesa local bus and PCI bus.
- DIP switch: These switches allow users to quickly toggle if it is used on PCB with other electronic parts. It customizes the behavior of an electronic device for specific situations.
- Heat Sink: The essential purpose of the heat sink is to transfer the heat generated by parts of the motherboard into a fluid medium like liquid or air. It is used to cool the CPU, GPU, Ram chipset, etc.
What are Motherboard Functions?
As we know, the motherboard is the central part of the computer. It performs the following functions:
- The most important parts of the computer are installed on the motherboard, like Processor, RAM, and hard drives.
- It transfers electricity to other parts of the PC.
- It forms a connection among the different devices of the system. It keeps the interference of the various components of the PC.
- It has expansion slots that install other hard drives and devices with it.
- Different forms and factors of the motherboard are different in size and configuration.
What is Motherboards Layout?
The form factor is the layout of the motherboard. ATX, Micro ATX, Mini ATX, and EATX form factors of the motherboards. All of them have different uses. The motherboard has many components, as described above.
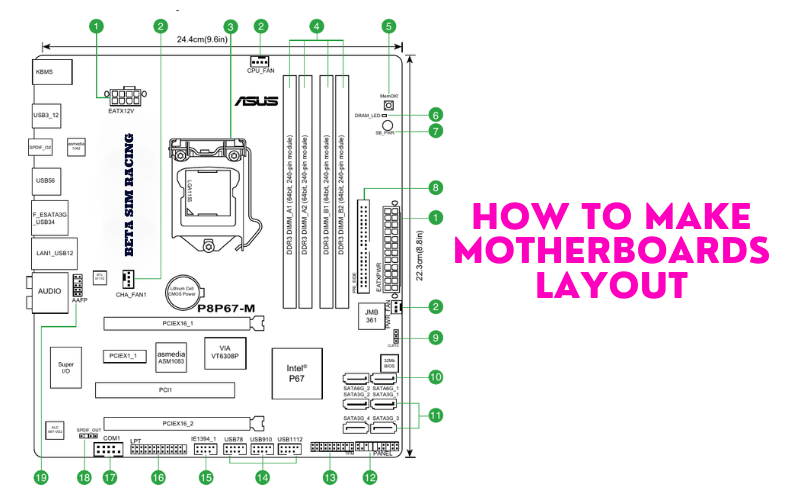
All the motherboards do not possess fan headers, BIOS batteries, and M.2 connectors. There are also various expansion slots according to the form factor of the motherboard. PCIe x16 slots are used for the Graphic card connection. PCIe x1 slots support various drives and cards.
RAM slots can be present according to the form factor of the motherboard. Most motherboards have two slots, but EATX motherboards can have up to 8 RAM slots. USB ports are found in different colors on the motherboard. You can find USB Gen 1, Gen 2, and Gen 3. The custom motherboard design will depend on the purpose of using that.
- Automated Optical Inspection: The AOI machine is used because components that are 2 mm cannot be checked by visual inspection. This machine checks and verifies parts with visible soldering points.
- Integrated Chip Tester: At last, every Chip that has soldering points below is verified by ICT. Like that chipset is soldering electrically to the board. Some tests are made by X-ray to check the quality of soldering.
- Wave Soldering: The motherboard keeps components on a side with pins through the PCB. The back of the PCB touches with wave solder, and these pins are soldered to attach the components to the board after the heat sink is mounted on the board before another inspection and checked by the ICT or integrated chip tester.
What Does the Motherboard Look Like?
A flat card-like structure with lots of metal connections and circuits using wires is a Motherboard. The motherboard is found inside the computer case with a processor on it.
How to Make a Motherboard Speaker?
It would help if you got a PC speaker to connect the speaker to the motherboard. It will have two wires and a round connector. You must read the motherboard manual to connect the speaker to the motherboard. You can find the procedure on the related website of the motherboard. See the location on the board where you can connect the speakers. Connect the speaker to the port. Speakers will have different types of connectors.
How to Make a Motherboard from Scratch?
Scratch is the website that offers to make a visual layout for your motherboard. It is a top leading community for teaching children about problem-solving and creative learning. It offers to make a motherboard layout and then print it on paper.
You can choose the form factor of your choice. It can be directly pasted on the metal by the adhesive spray. Cut the Design by using machines and then fix the components on it.
How to Build a Motherboard Circuit?
After completing the SMDs on the board, the motherboard goes to the reflow oven for the soldering process. The motherboard goes on with the different levels at a high temperature of 245 degrees. Electrical and mechanical connections are made at this point. After that, the visual inspection ensures no misplacement or missing parts.
The process of making the motherboard is easy for the experts. It will not be recommended to do for average users. The motherboard performs all the functions of the PC. There can be technical connections and delicate parts to be handled safely.
Final Conclusion

1 Comment
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.