In the intricate landscape of computer hardware, understanding your system’s memory configuration is pivotal for upgrades and optimal performance. This guide demystifies the process of finding out how many memory slots are populated on a motherboard without the need to crack open your computer case. From Windows 10 to Windows 11, we’ll explore efficient methods and commands to unveil the mysteries of your computer’s memory architecture.
How to Find How Many Memory Slots are in a Computer?
1) Checking System Information:
- Press Win + S to open the Windows search bar.
- Type “System Information” and select the corresponding result.
- In the System Information window, navigate to “System Summary” on the left.
- Look for an entry called “Installed Physical Memory (RAM)” and check the “Slots Used” information.

Explanation:
The System Information tool provides a quick overview of your system’s hardware, including details about the installed RAM and the number of slots in use.
Related Article:
2) Using Command Prompt:
- Press Win + S and type “Command Prompt” or “cmd.”
- Right-click on Command Prompt and select “Run as administrator.”
- In the Command Prompt window, type the command wmic memorychip get capacity, devicelocator, banklabel and press Enter.
- The output displays details about each memory module, including the bank label, which indicates the slot.
Explanation:
The wmic command taps into the Windows Management Instrumentation to fetch detailed information about the memory modules, including the slots they occupy.
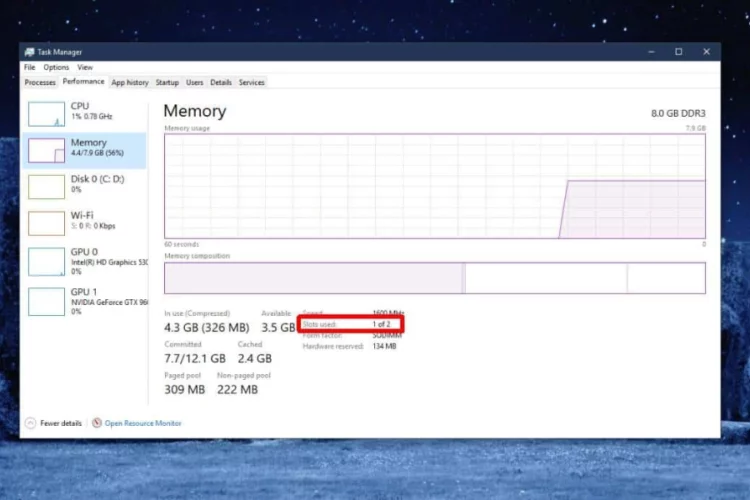
3) Checking Task Manager:
- Right-click on the taskbar and select “Task Manager.”
- Navigate to the “Performance” tab.
- Under the “Memory” section, click on “Slots Used.” This provides a quick snapshot of your occupied memory slots.
Explanation:
Task Manager offers a user-friendly interface for monitoring system performance, and the “Slots Used” feature simplifies the process of checking memory slots.
How to Quickly Determine Memory Slots Available on Motherboard on Windows 10?
For Windows 10 users, discovering available memory slots is a breeze with these steps:
1) Utilizing System Information:
- Follow the same steps as mentioned in the first method for checking System Information.
- Look for the “Slots Available” information under “System Summary.”
Explanation:
Windows 10’s System Information tool offers a comprehensive summary, including details about available memory slots.
2) Command Prompt Method:
Execute the same wmic memorychip get capacity, devicelocator, banklabel command in Command Prompt as detailed in the second method.
Explanation:
The command-line approach remains consistent across Windows versions, providing accurate details about your memory slots.
How to Check Available RAM Slots in Windows 11?
Navigating the new Windows 11 environment to discover available RAM slots is just as straightforward:
1) Leveraging System Information:
The process is identical to that in Windows 10. Open System Information and find the “Slots Available” information under “System Summary.”
Explanation:
Windows 11 inherits the System Information tool from its predecessor, maintaining a consistent method for exploring your system’s memory configuration.
2) Using the Command Prompt:
Execute the same wmic memorychip get capacity, devicelocator, banklabel command in Command Prompt, as detailed in the Windows 10 method.
Explanation:
The command-line approach remains a reliable method in Windows 11, delivering precise information about available memory slots.
Command to Check RAM Slots in Motherboard?
The command wmic memorychip get capacity, devicelocator, banklabel proves to be a versatile and powerful tool for checking RAM slots on both Windows 10 and Windows 11. This command extracts essential details about each memory module, including its capacity, device locator, and bank label, which indicates the specific slot on the motherboard.
Why is Knowing Available Memory Slots Important?
Understanding the number of memory slots and their occupancy is crucial for various reasons:
- Upgrades: Before expanding your system’s memory, knowing available slots guides the selection of compatible RAM modules.
- Troubleshooting: Identifying populated slots aids in troubleshooting issues related to specific memory modules.
- Optimization: Efficiently managing available memory slots ensures optimal system performance and resource utilization.
How can I find out if I have empty memory slots on my motherboard?
Use tools like System Information or Command Prompt on Windows to discover the number of occupied and available memory slots.
Can I use Task Manager to check memory slots on Windows 11?
Yes, Task Manager in Windows 11 provides a quick overview of occupied memory slots under the “Performance” tab.
Why is the number of memory slots essential for RAM upgrades?
Knowing the available slots ensures compatibility when upgrading RAM, preventing potential issues with mismatched modules.
Does the command wmic memorychip work on all Windows versions?
Yes, the wmic memorychip command is a versatile tool that works on various Windows versions, including Windows 10 and Windows 11.
Can I check memory slots on a laptop using these methods?
Yes, the described methods are applicable to both desktops and laptops running Windows 10 or Windows 11.
What if my memory slots information is not available in Task Manager?
In such cases, rely on System Information or Command Prompt for a more detailed overview of your memory configuration.