In the intricate landscape of computer hardware, the CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) holds a pivotal role, particularly in the form of CMOS RAM on a motherboard. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll unravel the mysteries surrounding CMOS, exploring its purpose, its collaboration with BIOS, and the significance of the CMOS battery. Join us on this journey to gain a deeper understanding of this crucial component that quietly influences your computer’s functionality.
Understanding CMOS
CMOS, or Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor, refers to the technology used in the creation of semiconductors. In the context of a computer, CMOS is synonymous with the CMOS battery and CMOS RAM found on the motherboard. It plays a crucial role in storing and maintaining essential information that ensures your computer functions smoothly.

Purpose of CMOS
The primary purpose of CMOS on a motherboard is to retain vital system configuration data, even when the computer is powered off. This information includes BIOS settings, date and time, hardware configurations, and other critical parameters. By preserving this data, CMOS ensures that your computer can boot up efficiently and operate according to your specified preferences.
How BIOS and CMOS Work Together?
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) and CMOS work hand in hand to initialize and configure the computer’s hardware components during the boot-up process. BIOS, a firmware interface, relies on the data stored in CMOS to understand the system’s configuration and load the operating system accordingly.
BIOS Settings in CMOS
CMOS holds the key to BIOS settings, allowing users to customize various parameters such as boot order, system date and time, and hardware configurations. Changes made in the BIOS setup are stored in the CMOS memory, ensuring that they persist even after the system is powered down.
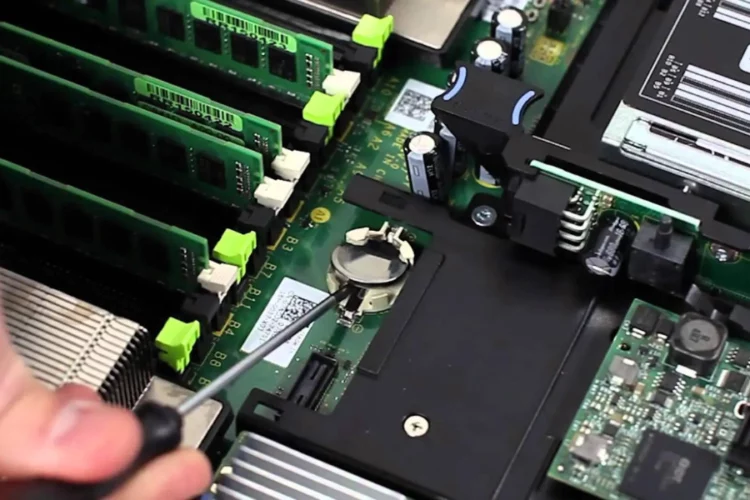
What Is a CMOS Battery?
The CMOS battery is a small, coin-shaped battery located on the motherboard. While the CMOS RAM is volatile memory and loses its data when power is cut off, the CMOS battery ensures a constant power supply to this memory, preventing the loss of critical information.
Lifespan and Replacement
Over time, CMOS batteries may lose their effectiveness, leading to issues such as date and time resets or BIOS configuration errors. Regularly replacing the CMOS battery is crucial to maintaining the integrity of stored data and preventing disruptions in your computer’s functionality.
Related Article: How Much RAM Do I Need for Mining?
What is CMOS Memory Usually Needed For?
Preserving System Settings
One of the primary functions of CMOS memory is to preserve system settings configured through the BIOS setup. This includes settings related to boot order, drive configurations, and hardware parameters, ensuring that your computer boots up with the desired specifications.
Date and Time Information
CMOS memory is responsible for storing the system’s date and time information. This may seem like a simple task, but accurate date and time settings are essential for various system functions, including file timestamps and scheduled tasks.
Hardware Configurations
Critical hardware configurations, such as the type and capacity of installed RAM, are stored in CMOS memory. This information is vital for the system to recognize and utilize hardware resources optimally.
What Is CMOS in Computer?
In the context of a computer, CMOS refers to both the technology used in creating semiconductors and the specific memory and battery system on the motherboard. This dual functionality underscores the integral role CMOS plays in preserving essential system information.
CMOS in Modern Computers
As technology advances, the role of CMOS remains crucial in modern computers. While newer storage technologies have emerged, CMOS continues to be the go-to solution for retaining volatile data that ensures seamless system operation.
Function of CMOS in Computer
The primary function of CMOS in a computer is to facilitate the boot-up process. When the computer is powered on, the data stored in CMOS, particularly the BIOS settings, is utilized by the system to initialize hardware components and load the operating system.
User Configuration Persistence
CMOS ensures that user-configured settings, such as those related to system preferences and hardware configurations, persist across power cycles. This feature is essential for maintaining a consistent and personalized computing experience.
What is the purpose of CMOS on a motherboard?
The purpose of CMOS on a motherboard is to retain critical system configuration data, including BIOS settings, date and time, and hardware configurations, to ensure efficient boot-up and consistent system operation.
What is CMOS memory usually needed for?
CMOS memory is usually needed for preserving system settings configured through the BIOS setup, storing date and time information, and retaining critical hardware configurations for optimal system operation.